Reception


Reception
Complete the tutorial to learn the controls of the game and explore educational presentations to develop an understanding of the importance of the aquaculture industry in Scotland, the nutritional benefits of seafood, and the characteristics of Atlantic salmon including their lifecycle and production cycle
What is aquaculture?
What is aquaculture?
Aquaculture is the rearing of animals and the cultivation of plants in any water environment. This can include:
- finfish such as salmon,
- shellfish such as mussels

- and algae such as seaweed (not covered in this course)
Why is aquaculture important to Scotland?
Why is aquaculture important to Scotland?
- The farming of Scotland’s seas contributes almost £500 million annually to the Scottish economy (Scottish Government 2021).
- Salmon is the largest food export in the UK, with >200 active farms harvesting >150,000 tonnes annually (Salmon Scotland 2023, Scottish Government 2022).
- By 2030 the number of jobs supported by the sector could reach 18,000. To thrive globally, the Scottish aquaculture sector needs a diverse workforce with the right skills - for 5 years’ time, 15 years’ time and beyond (Scotland Food and Drink 2017).
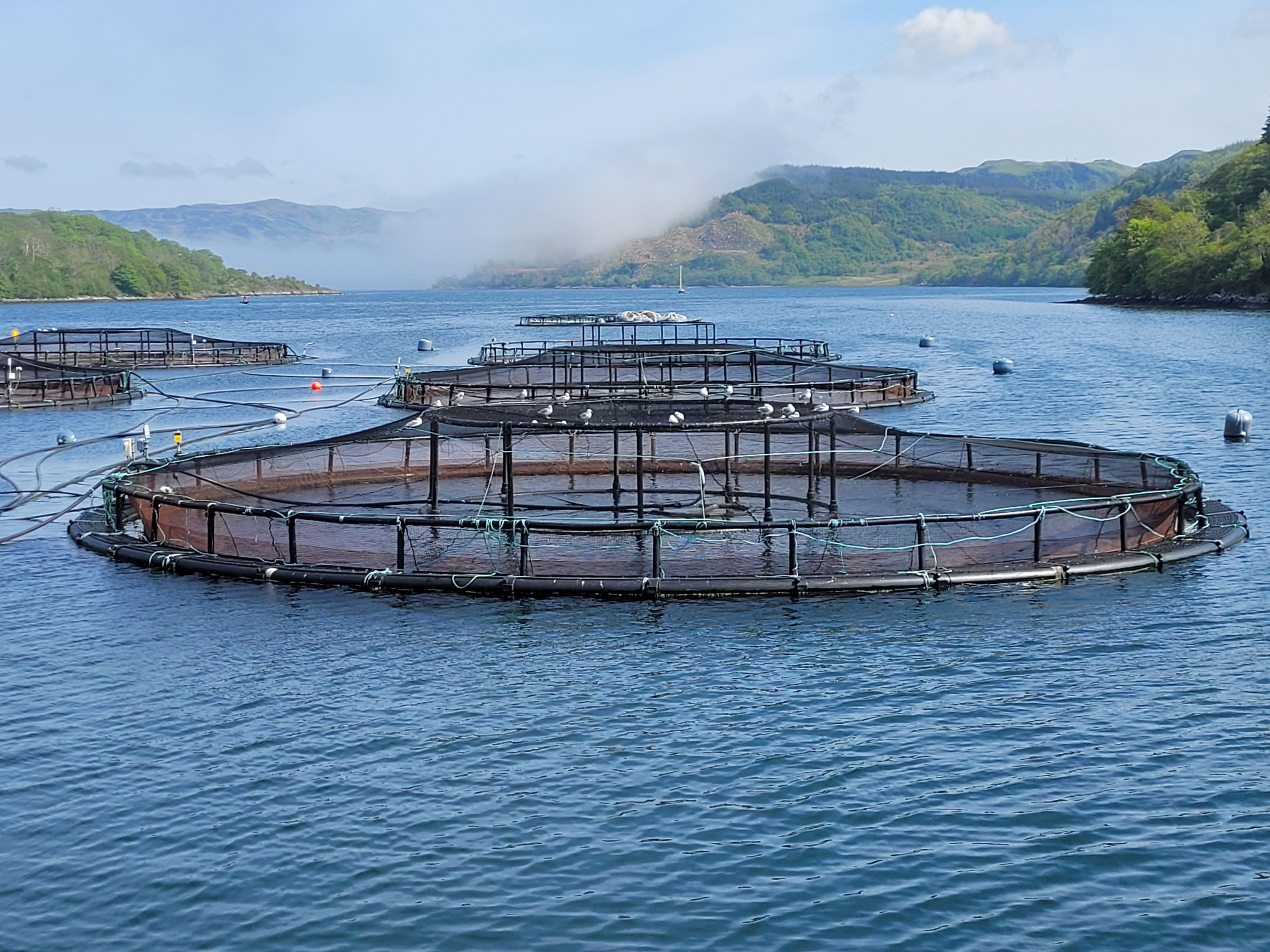

Nutritional benefits of seafood
Nutritional benefits of seafood
- A healthy, balanced diet should include at least 2 portions of fish a week, including 1 of oily fish.
- Fish such as salmon are good sources of many vitamins and minerals
- Oily fish – such as salmon and sardines –are particularly high in long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, which can help to keep your heart healthy.
- (NHS 2022)

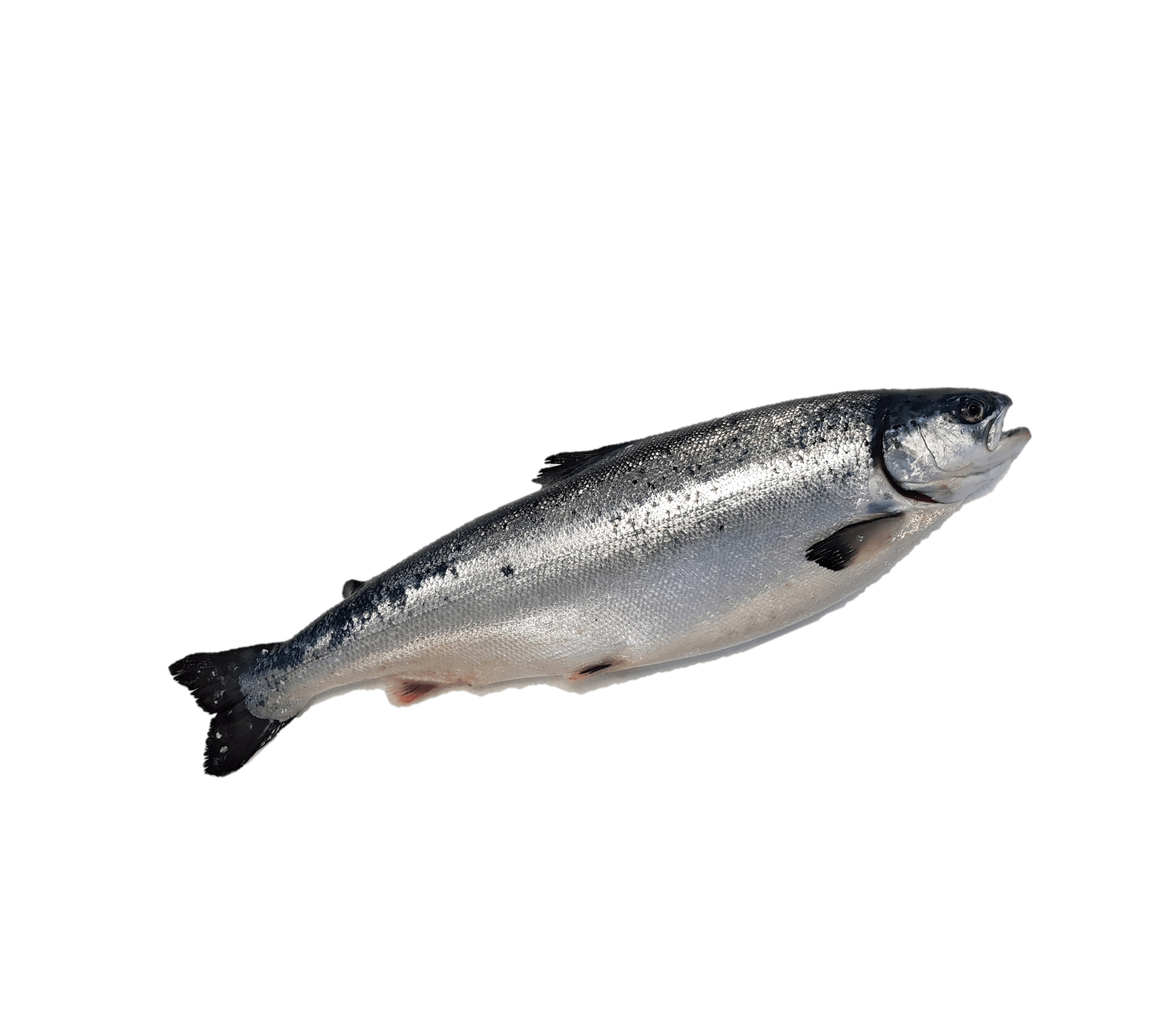
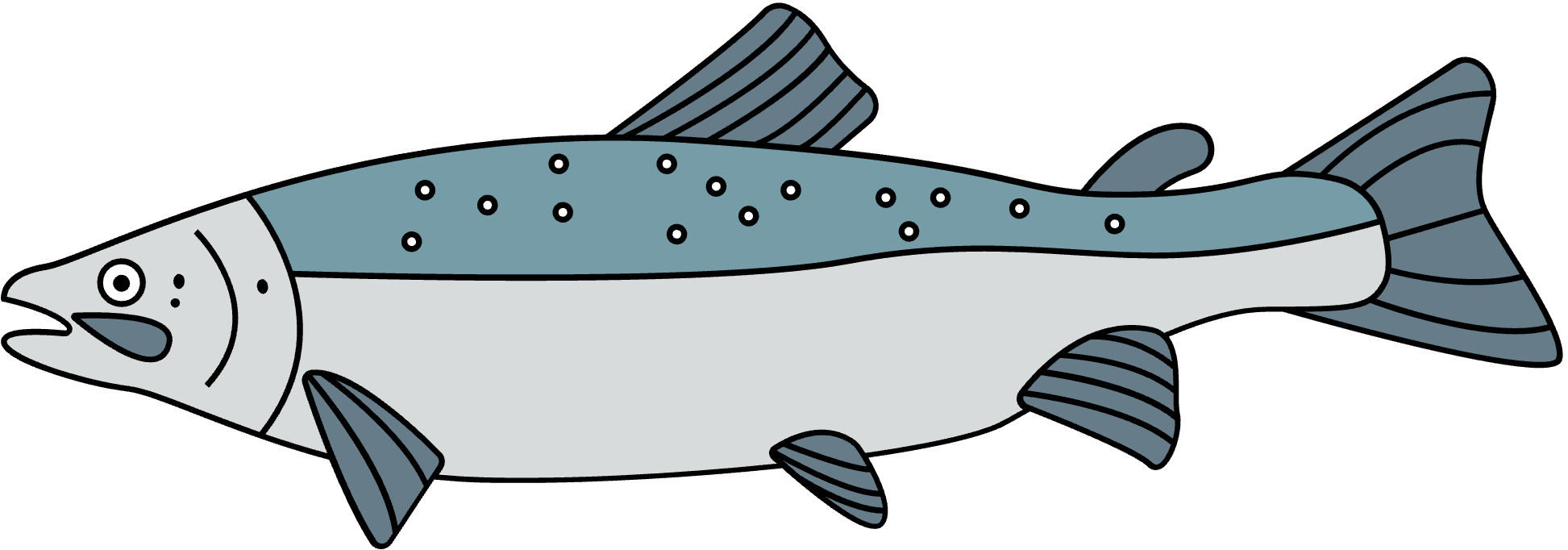
Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar)
Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar)
- Atlantic salmon, also known as the “king of fish” live in coastal seas and feed on pelagic invertebrates and some fishes.
- They are anadromous, meaning they migrate from the sea into fresh waters to spawn. This is the opposite of the common eel which leaves fresh waters to spawn in the sea and is instead called catadromous.
- They are an indicator species; the health of salmon populations closely reflects the status of their larger marine ecosystem.

The Salmon Lifecycle - In the Wild
The Salmon Lifecycle - In the Wild
1. Female salmon swim upstream to lay their eggs in cold freshwater as their eggs, alevins and fry cannot survive in the salty and unprotected conditions of the sea. They are buried in gravel and the flow of running water provides a source of oxygen.
2. Juvenile salmon (parr) only have the physiological mechanisms needed for surviving in freshwater. However, as smolt they migrate downstream to the estuary and ocean. They must therefore adapt their kidney function to cope with the salt-water conditions and develop protective silvery scales.
3. Most salmon spend the first part of their adult life in coastal waters, they then migrate further out to sea where they spend from 1 to 7 years. They can travel up to 50km a day in a large school and return to their home stream or lake to breed.
Quiz
Quiz
Why is aquaculture important to Scotland?
- The farming of Scotland's seas contributes over _________ annually to the Scottish economy (Scottish Government 2021).
- Salmon is the second largest food export in the UK, after whisky with _______ active farms harvesting _______ tonnes annually.
- _______% of all Scottish mussels are grown in Shetland.
- By 2030 the number of jobs supported by the sector could reach ________. To thrive globally, the Scottish aquaculture sector needs a diverse workforce with the right skills - for 5 years time, 15 years time and beyond.
Nutritional benefits of seafood
5. How many portions of fish a week should a healthy, balanced diet ideally include?
A.1, B.2, C.4, or D.6
6. What are fish and shellfish good sources of?
A. Zinc, B. Omega-3, C. Iodine, D. Vitamins, E. Omega-3 and vitamins, F. Omega-3 and iodine, G. all of the above
Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar)
7. What is the nickname often given to Atlantic salmon?
A. Prince of the waters, B. Silver bellies, C. King of the Fish, D. Slippery fins
8. Where can the species be found?
A. Far offshore, B. Coastal seas